1. Hierarchical Attention Networks for Document Classification
Source: https://www.cs.cmu.edu/~./hovy/papers/16HLT-hierarchical-attention-networks.pdf
Authors: Zichao Yang, Diyi Yang, Chris Dyer, Xiaodong He, Alex Smola, Eduard Hovy
Topics: deep learning, NLP, text classification
Text classification is the process of assigning categories or tags to text according to its content.
It is one of the fundamental tasks in NLP with broad applications such as sentiment analysis, spam detection, intent detection, and topic labeling.
About 80% of all information is unstructured, with text being one of the most common types of unstructured data.
Many businesses will benefit from robust text classifiers to structure information such as email messages, social media messages, legal documents, web pages, and chat conversations.
This paper proposes a model called Hierarchical Attention Networks (HAN) to classify documents into some labels such as topics or discrete ratings.
It is a temporal sequence model that consists of two stacked modules: word and sentence modules, respectively.
Each module has an encoding layer followed by an attention layer.
The encoding layer is actualized by bidirectional GRU, a type of recurrent neural networks.
“Bidirectional” implies that the sequence model is encouraged to capture both past and future temporal coherences.
Attention layer is applied on the top of that, which is a shallow neural network that perfoms a kind of soft-pooling.
The output of the attention layer is a weighted linear combination of its input vectors, the weights of which are learned from data.
HAN architecture is illustrated below.
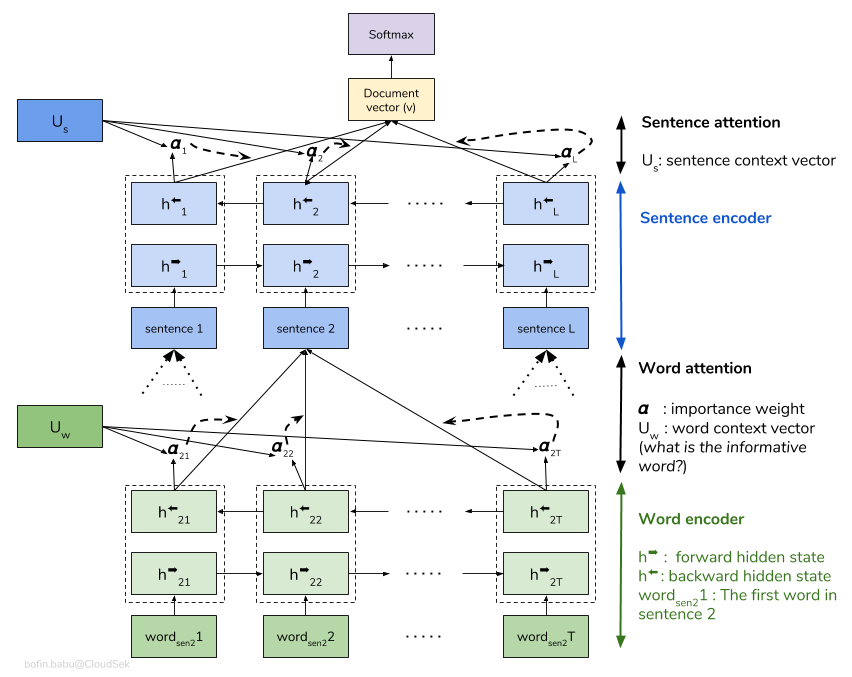
HAN architecture (source: https://medium.com/analytics-vidhya/hierarchical-attention-networks-d220318cf87e)
The model was evaluated over a wide range of datasets such as Yelp reviews, IMBD reviews, Yahoo answers, and Amazon reviews.
The results demonstrate that HAN performs significantly better than some previously proposed text classifiers.
As a bonus, the weights learned in the attention layers can provide an interesting visualization indicating word and text saliencies.

2. Combining Knowledge with Deep Convolutional Networks for Short Text Classification
Source: https://www.ijcai.org/proceedings/2017/0406.pdf
Authors: Jin Wang, Zhongyuan Wang, Dawei Zhang, Jun Yan
Short-text classification is a special case of text classification tasks.
It has gained substantial interest, especially due to the rise of Internet, mobile, e-Commerce, and social media applications in which the user-generated texts are typically short.
Despite the impressive progress in the text classification realm, particularly driven by more advanced text representation engineering and/or learning,
there are still some limitations for classifying short texts – below are the verbatim remarks from the paper:
- Unlike paragraphs or documents, short texts do not always observe the syntax of natura language;
- Short texts lack of contexts;
- Short texts are usually rather ambiguous because they contain polysemes and typos.
This paper proposes a method that first enrich the information of short texts by utilizing an explicit knowledge base. i.e., by creating association between each short text and its relevant concepts in the knowledge base.
It then generates the implicit representation through word embedding learning that incorporates the enriched texts.
Futhermore, it also takes into account the character-level representation to acquire more sub-word information such as morphemes, which are non-existent in word-level representations.
The resulting model architecture is shown in the figure below, which is named as Knowledge Powered Convolutional Neural Network (KPCNN).
The model consists of two sub-networks: 1) word-level CNN and 2) character-level CNN, which are trained jointly in the context of end-to-end classification tasks.
The word-level CNN is equipped with word embedding layer pretrained from the enriched texts: words and their concepts – the embedding layer is kept being static during the joint training.
Meanwhile, the character-level CNN does not have pre-trained embedding layer and, therefore, during the joint training its parameters are updated.
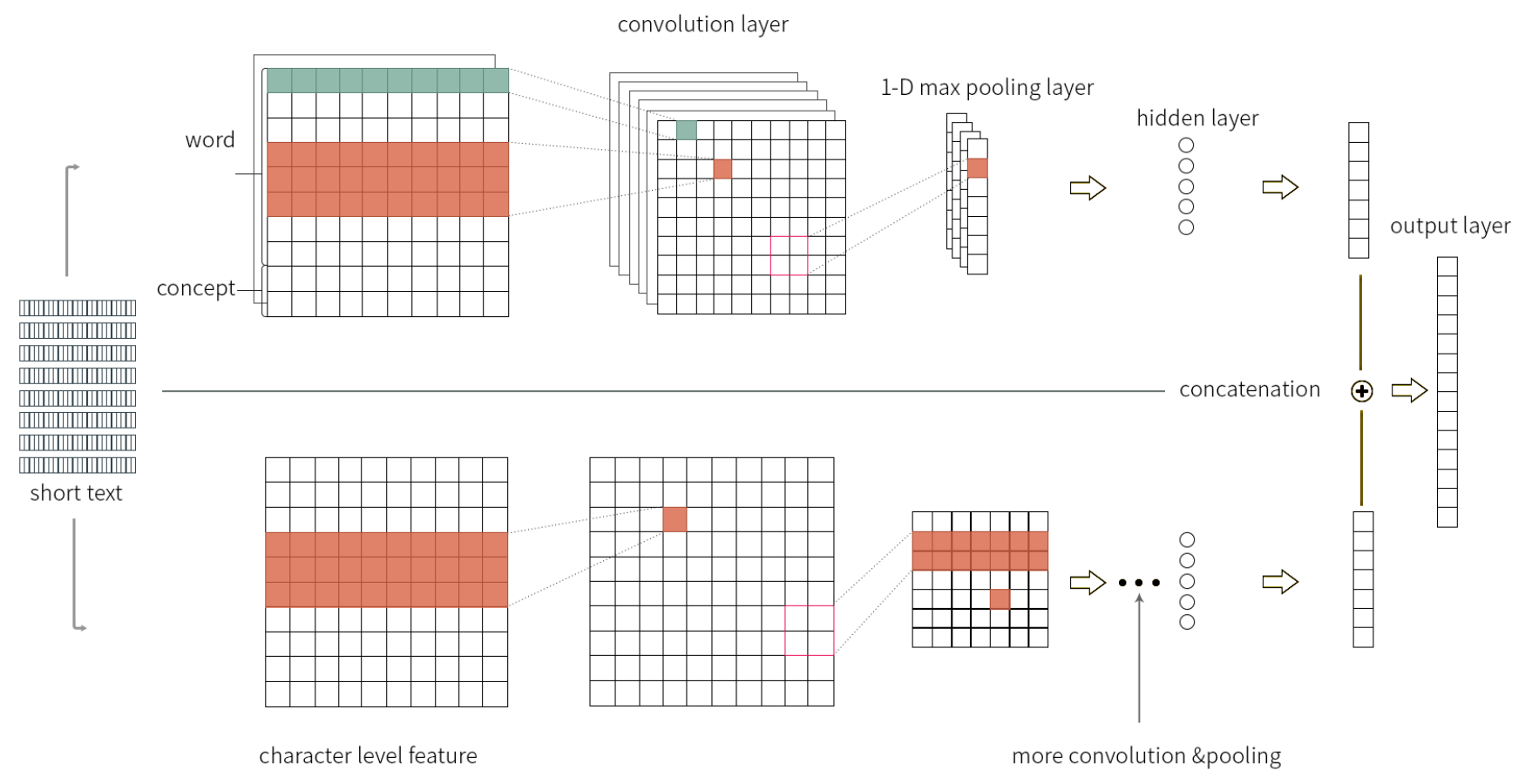
The method was evaluated on several benchmarks for short text classification tasks such as TREC, Twitter, AG news, Bing, and Movie Review.
The results show its superiority over some other state-of-the-art methods.
3. How can AI revive retail
Source: https://www.juniperresearch.com/document-library/white-papers/how-ai-can-revive-retail
Authors: Juniper Research
Topics: artificial intelligence, retail
This whitepaper presents a study from Juniper Research about the impact of AI services in retail.
Under a premise that retailers must adopt AI solutions to save them from the advanced competition,
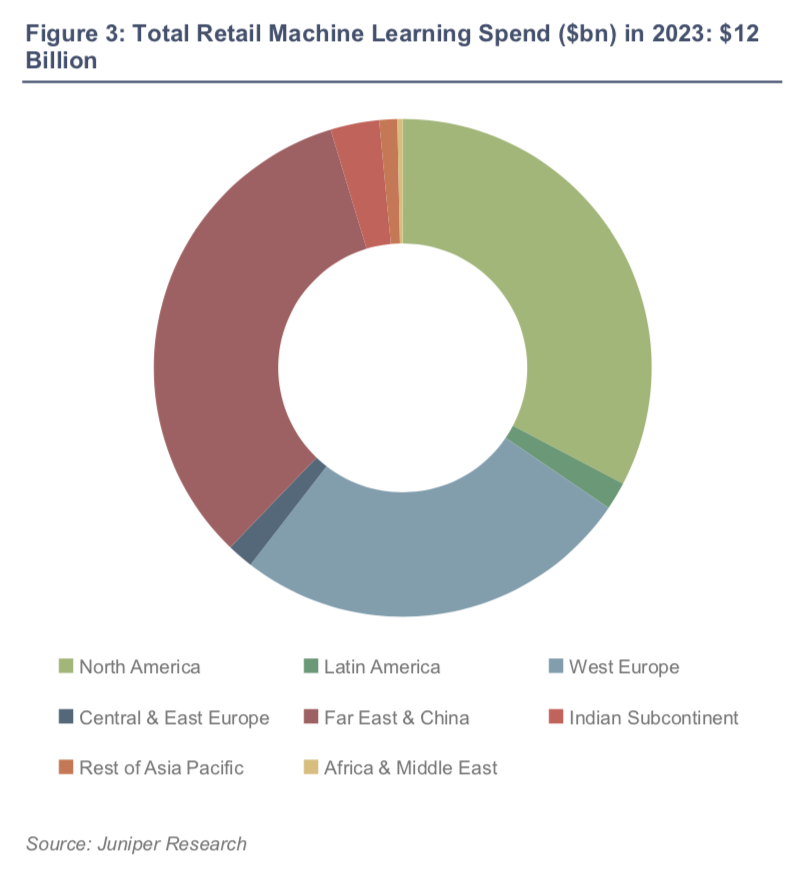
the global spending in adopting AI technologies by retailers is estimated to increase by 230% between 2019 and 2023 – from \(\$3.6\) billion in 2019 to \(\$12\) billion by 2023.
Juniper expects over 325,000 retailers to adopt AI technology over the period.
Some AI areas of interest that have the potential to revive retail are as follows:
- Personalisation: creating more personalized customer experience, boosting the quality of customer interactions and making a browser more likely to be a purchaser
- Demand Forecasting / Supply Chain Analytics: understanding future trends / demans to ensure that the stock supply is always available.
- Customer Analytics and Marketing: understanding customer sentiment/intent and marketing them based on that.
- Payment Provider Analytics: understanding retailers’ sales pattern through payment history.
- Chatbots: delivering more efficient customer service / engagement reducing the needs of human experts.
The use of AI for demand forecasting will prove to be a key retailer’s demand.
This will be an opportunity for AI vendors in providing that need,
with revenues reaching \(\$3\) billion by 2023, up from \(\$760\) million in 2019.
Demand forecasting will be essential to enable an effective omnichannel experience and drive higher margins.